
INFORMATION
Knee joint replacement
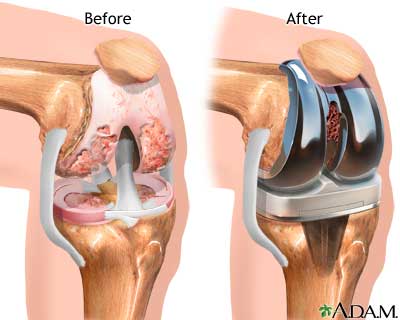
Knee replacement, also called knee arthroplasty or total knee replacement, is a surgical procedure to resurface a knee damaged by arthritis. Metal and plastic parts are used to cap the ends of the bones that form the knee joint, along with the kneecap. This surgery may be considered for someone who has severe arthritis or a severe knee injury.
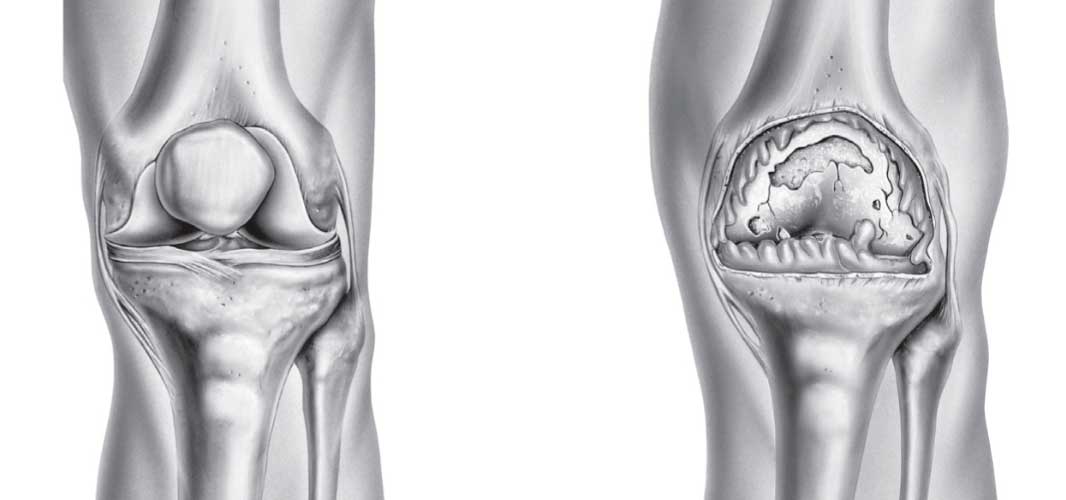
Various types of arthritis may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects mostly middle-aged and older adults, may cause the breakdown of joint cartilage and adjacent bone in the knees. Rheumatoid arthritis, which causes inflammation of the synovial membrane and results in excessive synovial fluid, can lead to pain and stiffness. Traumatic arthritis, arthritis due to injury, may cause damage to the cartilage of the knee.
The goal of knee replacement surgery is to resurface the parts of the knee joint that have been damaged and to relieve knee pain that cannot be controlled by other treatments.
Reasons for the procedure
Knee replacement surgery is a treatment for pain and disability in the knee. The most common condition that results in the need for knee replacement surgery is osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage. Damage to the cartilage and bones limits movement and may cause pain. People with severe degenerative joint disease may be unable to do normal activities that involve bending at the knee, such as walking or climbing stairs, because they are painful. The knee may swell or “give-way” because the joint is not stable.
Other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis that results from a knee injury, may also lead to degeneration of the knee joint. In addition, fractures, torn cartilage, and/or torn ligaments may lead to irreversible damage to the knee joint.
If medical treatments are not satisfactory, knee replacement surgery may be an effective treatment.
Most of the time, knee joint replacement is done in people age 60 and older. Younger people who have a knee joint replaced may put extra stress on the artificial knee and cause it to wear out early and not last as long.
Before the Procedure
Always tell your health care provider what drugs you are taking, even drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription.
During the 2 weeks before your surgery:
- Prepare your home
- Two weeks before surgery, you may be asked to stop taking drugs that make it harder for your blood to clot. These include aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve), blood thinners such as warfarin (Coumadin), or clopidogrel (Plavix), and other drugs.
- You may also need to stop taking medicines that can make your body more likely to get an infection. These include methotrexate, Enbrel, or other medicines that suppress your immune system.
- Ask your provider which drugs you should still take on the day of your surgery.
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical conditions, your surgeon may ask you to see the provider who treats you for these conditions to see if it is safe for you to have the surgery.
- Tell your provider if you have been drinking a lot of alcohol, more than 1 or 2 drinks a day.
- If you smoke, you need to stop. Ask your providers for help. Smoking will slow down wound and bone healing. Your recovery may not be as good if you keep smoking.
- Always let your provider know about any cold, flu, fever, herpes breakout, or other illness you have before your surgery.
- You may want to visit a physical therapist to learn some exercises to do before surgery.
- Set up your home to make everyday tasks easier.
- Practice using a cane, wlker, crutches, or a wheelchair correctly.
On the day of your surgery:
- You will most often be asked not to drink or eat anything for 6 to 12 hours before the procedure.
- Take the drugs you have been told to take with a small sip of water.
- You will be told when to arrive at the hospital.
After the Procedure
You will stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days. During that time, you will recover from your anesthesia and from the surgery itself. You will be asked to start moving and walking as soon as the first day after surgery.
Full recovery will take 4 months to a year.
Some people need a short stay in a rehabilitation center after they leave the hospital and before they go home. At a rehabilitation center, you will learn how to safely do your daily activities on your own.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The results of a total knee replacement are often excellent. The operation relieves pain for most people. Most people DO NOT need help walking after they fully recover.
Most artificial knee joints last 10 to 15 years. Some last as long as 20 years before they loosen and need to be replaced again. Total knee replacements can be replaced again if they get loose or wear out. However, in most cases the results are not as good as the first time. It is important not to have the surgery too early so you will need another surgery at a young age or have it too late when you will not benefit the most.
Getting your home ready – knee or hip surgery
Before you go to the hospital for surgery, set up your home to make your recovery and life easier when you come back. Do this well in advance of your surgery.
Make It Easy for Yourself
Make sure everything you need is easy to get to and on the floor where you will spend most of your time. Limit your stair use to once a day.
- Have a bed that is low enough so that your feet touch the floor when you sit on the edge of the bed.
- Set up your bed on the first floor if you can. You may not need a hospital bed, but your mattress should be firm.
- Have a bathroom or a portable commode on the same floor where you will spend most of your day.
- Stock up on canned or frozen food, toilet paper, shampoo, and other personal items.
- Make or buy single meals that can be frozen and reheated.
- Make sure you can reach everything you need without getting on your tiptoes or bending down low.
- Put food and other supplies in a cupboard that is between your waist and shoulder level.
- Place glasses, your teapot, and other items you use a lot on the kitchen counter.
- Make sure you can get to your phone. A portable phone can be helpful.
- Place a chair with a firm back in the kitchen, bedroom, bathroom, and other rooms you will use. This way, you can sit when you do your daily tasks.
- If you will be using a walker, attach a sturdy bag or a small basket. Put in it the things you need to have close by such as your phone, a notepad, a pen, and other necessary items. You can also use a fanny pack.
- You may need to have safety bars in your bathroom. Grab bars should be secured vertically or horizontally to the wall, not diagonally.
You may need help bathing, using the toilet, cooking, running errands, shopping, going to provider visits, and exercising. If you do not have someone to help you at home for the first 1 or 2 weeks after surgery, ask your provider about having a trained caregiver come to your home. This person can also check the safety of your home and help you with your daily activities.
You may need to have safety bars in your bathroom. Grab bars should be secured vertically or horizontally to the wall, not diagonally.
How long are you out of work after a total knee replacement?
Most doctors recommend about six weeks. Your ability to return to work depends on your job requirements. Patients with physically demanding jobs are often out of work for three to six months. Patients who hold desk jobs or administrative positions may return to work within six weeks, but this is the minimum.
What activities can you not do after knee replacement?
Doctors have long recommended that knee replacement patients avoid sports like football, soccer, aerobics, jogging, baseball and basketball because it was thought that high-impact activities might contribute to the early failure of artificial joints, leading to the need for a second surgery.
How much can you lift after knee replacement?
Even if you’re able to return to full normal after your surgery, you’ll need to mind your artificial knee for the rest of your life. Avoid lifting anything more than 20 pounds.
How far should I walk after knee replacement?
You will probably use a walker for 1 to 3 weeks and then use crutches. When you are ready, you can use a cane. You will probably be able to walk on your own in 4 to 8 weeks. You will need to do months of physical rehabilitation (rehab) after a knee replacement.
Is walking good after knee replacement?
Walk as much as you would like but remember that walking is no substitute for the exercises prescribed by your doctor and physical therapist. Swimming is an excellent low-impact activity after a total knee replacement; you can begin swimming as soon as the wound is sufficiently healed.
NOTE: This information is intended to provide an overview of a surgery. It is not and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical care or a discussion between you and your surgeon about the need for surgery. Specific recommendations may vary among healthcare professionals. If you have any questions about your need for surgery, your alternatives, or the training and experience of your surgeons, feel free to do your own research. If you have questions about your surgery or postoperative period, always discuss them with your surgeon before or after your surgery.





