
INFORMATION
Rotator Cuff Surgery
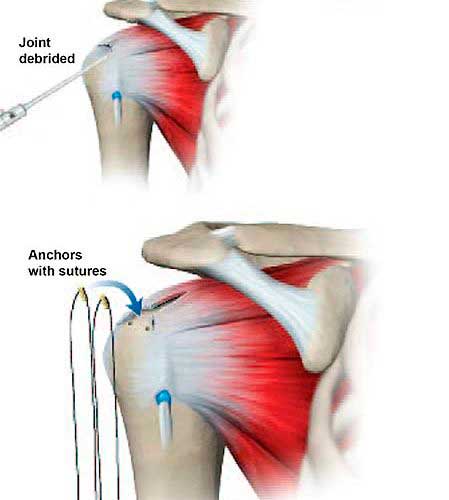
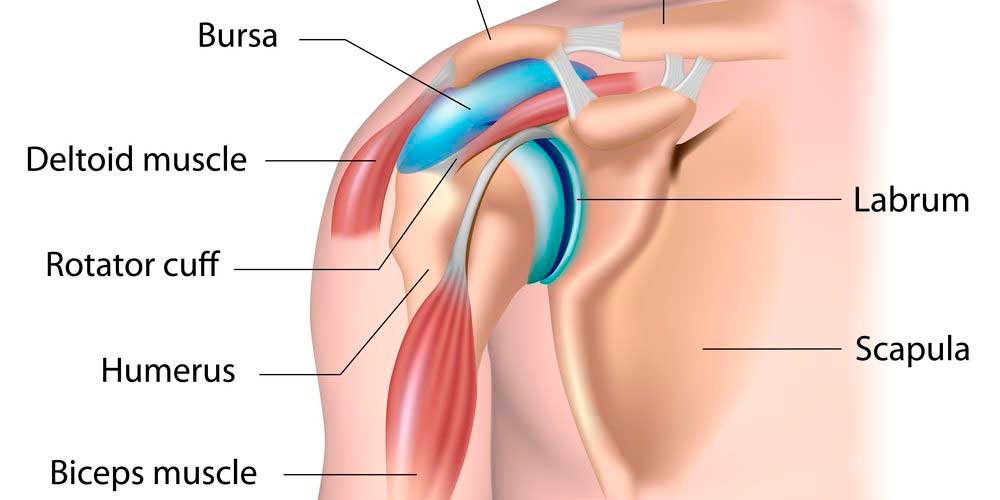
Surgery to repair a torn rotator cuff most often involves re-attaching the tendon to the head of humerus (upper arm bone). A partial tear, however, may need only a trimming or smoothing procedure called a debridement. A complete tear is repaired by stitching the tendon back to its original site on the humerus.
When Rotator Cuff Surgery is Recommended
Your doctor may offer surgery as an option for a torn rotator cuff if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. Continued pain is the main indication for surgery. If you are very active and use your arms for overhead work or sports, your doctor may also suggest surgery.
Other signs that surgery may be a good option for you include:
- Your symptoms have lasted 6 to 12 months
- You have a large tear (more than 3 cm) and the quality of the surrounding tendon tissue is good
- You have significant weakness and loss of function in your shoulder
- Your tear was caused by a recent, acute injury
Surgical Repair
The type of repair performed depends on several factors, including your surgeon’s experience and familiarity with a particular procedure, the size of your tear, your anatomy, and the quality of the tendon tissue and bone.
Many surgical repairs can be done on an outpatient basis and do not require you to stay overnight in the hospital.
You may have other shoulder problems in addition to a rotator cuff tear, such as biceps tendon tears, osteoarthritis, bone spurs, or other soft tissue tears. During the operation, your surgeon may be able to take care of these problems, as well.
The three techniques most commonly used for rotator cuff repair include traditional open repair, arthroscopic repair, and mini-open repair. In the end, patients rate all three repair methods the same for pain relief, strength improvement, and overall satisfaction.
All-Arthroscopic Repair
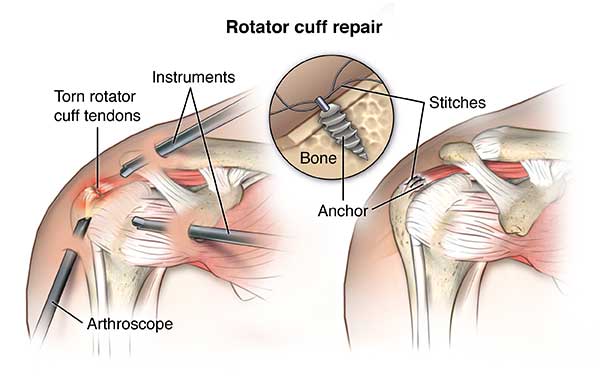
During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your shoulder joint. The camera displays pictures on a television screen, and your surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments.
Because the arthroscope and surgical instruments are thin, your surgeon can use very small incisions (cuts), rather than the larger incision needed for standard, open surgery.
All-arthroscopic repair is usually an outpatient procedure and is the least invasive method to repair a torn rotator cuff.
Recovery
PAIN MANAGEMENT
After surgery, you will feel pain. This is a natural part of the healing process. Your doctor and nurses will work to reduce your pain, which can help you recover from surgery faster.
Medications are often prescribed for short-term pain relief after surgery.
Talk to your doctor if your pain has not begun to improve within a few weeks after your surgery.
And don’t forget about icing the shoulder. Ice application may be the most important part of pain control.
SLEEPING AT NIGHT
Many patients find it most comfortable to sleep in a semi-upright position after rotator cuff surgery; a recliner is perfect. If you don’t have a recliner, just get a lot of pillows and create a backrest in bed to allow you to sleep in a seated position with the elbow pointing down.
How long does it take to recover from rotator cuff surgery?
4 to 6 months
Recovery can take 4 to 6 months, depending on the size of the tear and other factors. You may have to wear a sling for 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. Pain is usually managed with medicines. Physical therapy can help you regain the motion and strength of your shoulder.
REHABILITATION
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in getting you back to your daily activities. A physical therapy program will help you regain shoulder strength and motion.
Immobilization. After surgery, therapy progresses in stages. At first, the repair needs to be protected while the tendon heals. To keep your arm from moving, you will most likely use a sling and avoid using your arm for the first 4 to 6 weeks. How long you require a sling depends upon the severity of your injury.
Outcome
The majority of patients report improved shoulder strength and less pain after surgery for a torn rotator cuff.
Each surgical repair technique (open, mini-open, and arthroscopic) has similar results in terms of pain relief, improvement in strength and function, and patient satisfaction.
Factors that can decrease the likelihood of a satisfactory result include:
- Poor tendon/tissue quality
- Large or massive tears
- Poor patient compliance with rehabilitation and restrictions after surgery
- Patient age (older than 65 years)
- Smoking and use of other nicotine products
- Workers’ compensation claims
What is the fastest way to recover from shoulder surgery?
5 Tips to Speed Your Recovery from Rotator Cuff Surgery
- Wear your shoulder immobilizer or sling. After your procedure, your doctor will give you a sling or shoulder immobilizer to restrict your arm movement. …
- Participate in physical therapy. …
- Eliminate pain medication as quickly as possible. …
- Avoid certain shoulder positions and arm movements. …
- Don’t rush your recovery.
How soon can you drive after rotator cuff surgery?
You‘ll need rehab after rotator cuff surgery. This will start at 1 to 4 weeks and lasts 4 to 6 months. You cannot drive a car for 6 weeks, and it may take 4 weeks to return to work if you have a desk job. If you have to lift at work, you‘ll need to wait at least 3 months
How soon after rotator cuff surgery can I start physical therapy?
Rotator cuff surgery recovery usually consists of immobilizing the shoulder in a sling for seven to ten days, physical therapy with passive and assisted motion for six weeks, followed by physical therapy with active motion for six weeks
What are the symptoms of a failed rotator cuff surgery?
A shoulder surgery has failed when it does not achieve the expectations of the patient and the surgeon. Failure can result from stiffness, weakness, instability, pain or failure to heal, and from complications such as infection or nerve injury.





