INFORMATION
An upper endoscopy is a procedure used to visually examine your upper digestive system with a tiny camera on the end of a long, flexible tube. A specialist in diseases of the digestive system (gastroenterologist) uses an endoscopy to diagnose and, sometimes, treat conditions that affect the esophagus, stomach and beginning of the small intestine (duodenum).
The medical term for an upper endoscopy is esophagogastroduodenoscopy. You may have an upper endoscopy done in your doctor’s office, an outpatient surgery center or a hospital.
An upper endoscopy is used to diagnose and, sometimes, treat conditions that affect the upper part of your digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach and beginning of the small intestine (duodenum)
Your doctor may recommend an endoscopy procedure to:
- Investigate signs and symptoms.An endoscopy may help your doctor determine what’s causing digestive signs and symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Your doctor may use an endoscopy to collect tissue samples (biopsy) to test for diseases and conditions, such as anemia, bleeding, inflammation, diarrhea or cancers of the digestive system.
- Your doctor can pass special tools through the endoscope to treat problems in your digestive system, such as widening a narrow esophagus, clipping off a polyp or removing a foreign object.
An endoscopy is sometimes combined with other procedures, such as an ultrasound. An ultrasound probe may be attached to the endoscope to create specialized images of the wall of your esophagus or stomach. An endoscopic ultrasound may also help your doctor create images of hard-to-reach organs, such as your pancreas. Newer endoscopes use high-definition video to provide clearer images.
Many endoscopes have technology called narrow band imaging, which uses special light to help doctors better detect precancerous conditions, such as Barrett’s esophagus.
Risks
An endoscopy is a very safe procedure. Rare complications include:
- Tearing of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Reaction to sedation.
You can reduce your risk of complications by carefully following your doctor’s instructions for preparing for an endoscopy, such as fasting and stopping certain medications.
Signs and symptoms to watch for after your endoscopy include:
- Fever
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Bloody, black or very dark colored stool
- Difficulty swallowing
- Severe or persistent abdominal pain
- Vomiting, especially if your vomit is bloody or looks like coffee grounds
Call your doctor immediately or go to an emergency room if you experience any of these signs or symptoms.
How you prepare
Your doctor will give you specific instructions to prepare for your endoscopy.
Food and medications
You will need to stop drinking and eating up to eight hours before your endoscopy to ensure your stomach is empty for the procedure.
Tell your doctor about all the medications and supplements you’re taking before your endoscopy. If you take certain blood-thinning medications, your doctor may recommend that you stop taking them in the days before your endoscopy. Blood thinners may increase your risk of bleeding if certain procedures are performed during the endoscopy.
If you have chronic conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease or high blood pressure, your doctor will give you specific instructions regarding your medications.
Precautions
MOST PEOPLE UNDERGOING AN UPPER ENDOSCOPY WILL RECEIVE A SEDATIVE TO RELAX THEM AND MAKE THEM MORE COMFORTABLE DURING THE PROCEDURE. YOU MAY FEEL MENTALLY ALERT, BUT YOUR MEMORY, REACTION TIMES AND JUDGMENT MAY BE IMPAIRED. PLAN ON ALLOWING 24 HOURS FOR THE SEDATIVE TO WEAR OFF. AFTERWARD, YOU MAY RESUME YOUR NORMAL ACTIVITIES. ARRANGE FOR SOMEONE TO DRIVE YOU HOME AFTER THE PROCEDURE. YOU MAY ALSO NEED TO TAKE THE DAY OFF FROM WORK.
During the procedure
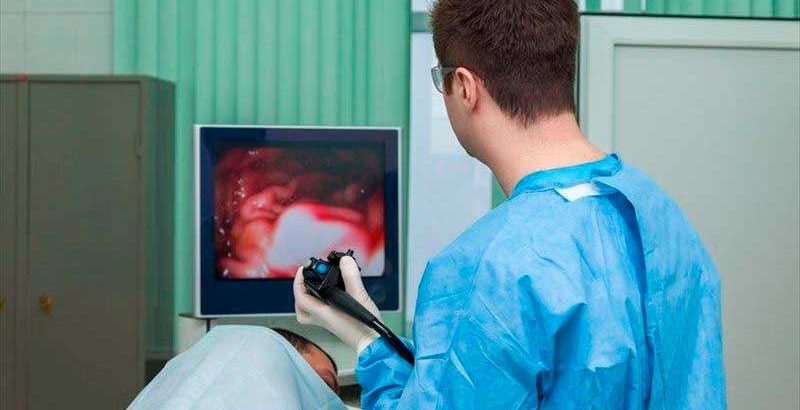
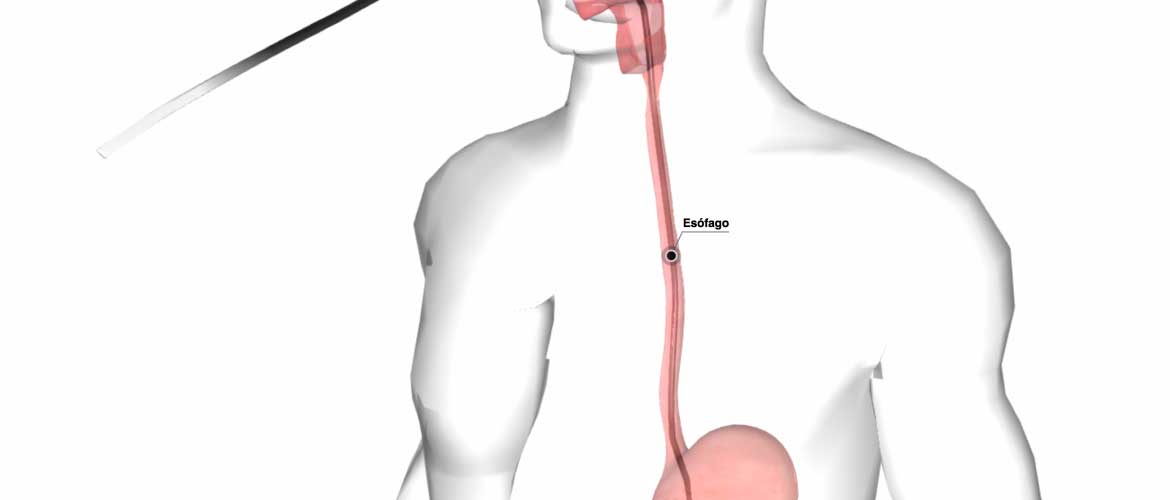
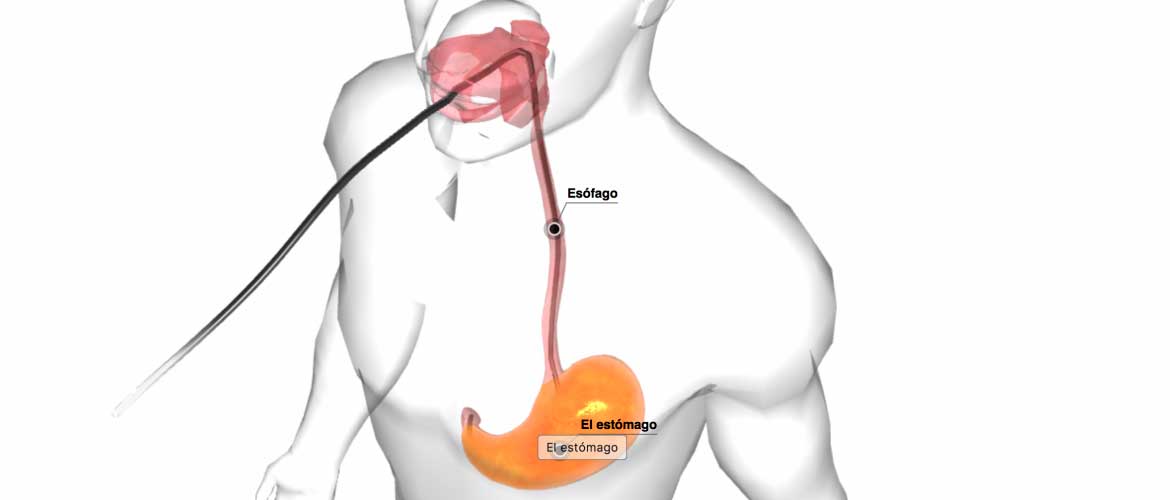
Your doctor will then insert the endoscope in your mouth. He or she may ask you to swallow as the scope passes down your throat. You may feel some pressure in your throat, but you generally shouldn’t feel pain.
You can’t talk after the endoscope passes down your throat, though you can make noises. The endoscope doesn’t interfere with your breathing.
As your doctor passes the endoscope down your esophagus:
- A tiny camera at the tip transmits images to a video monitor in the exam room.Your doctor watches this monitor to look for abnormalities in your upper digestive tract. If abnormalities are found in your digestive tract, your doctor may record images for later examination.
- Gentle air pressure may be fed into your esophagus to inflate your digestive tract.This allows the endoscope to move freely. And it allows your doctor to more easily examine the folds of your digestive tract. You may feel pressure or fullness from the added air.
- Your doctor will pass special surgical tools through the endoscope to collect a tissue sample or remove a polyp.Your doctor watches the video monitor to guide the tools.
When your doctor has finished the exam, the endoscope is slowly retracted through your mouth. An endoscopy typically takes 15 to 30 minutes, depending on your situation.
After the procedure
You’ll be taken to a recovery area to sit or lie quietly after your endoscopy. You may stay for an hour or so. This allows your health care team to monitor you as the sedative begins to wear off.
Once you’re at home, you may experience some mildly uncomfortable signs and symptoms after endoscopy, such as:
- Bloating and gas
- Cramping
- Sore throat
These signs and symptoms will improve with time. If you’re concerned or quite uncomfortable, call your doctor.
Take it easy for the rest of the day after your endoscopy. After receiving a sedative, you may feel alert, but your reaction times are affected and judgment is impaired.
Results
When you receive the results of your endoscopy will depend on your situation. If, for instance, your doctor performed the endoscopy to look for an ulcer, you may learn the findings right after your procedure. If he or she collected a tissue sample (biopsy), you may need to wait a few days to get results from the testing laboratory. Ask your doctor when you can expect the results of your endoscopy.
Is it painful to do an endoscopy?
The endoscopy procedure. An endoscopy isn’t usually painful, and most people only experience some mild discomfort, similar to indigestion or a sore throat. The procedure is usually carried out while you’re conscious. … The endoscope will be carefully inserted into your body.
How long does it take to recover from an endoscopy?
An upper endoscopy takes approximately 10 to 15 minutes. A colonoscopy takes approximately 15 to 30 minutes. How long will I be there after the procedure? Patients remain in the recovery area 30 to 40 minutes after their procedure.
Can you eat after a endoscopy?
Over the next 24-48 hours, eat small meals consisting of soft, easily-digestible foods like soups, eggs, juices, pudding, applesauce, etc. You should also avoid consuming alcohol for at least 24 hours after your procedure. When you feel like you’re “back to normal,” you may resume your normal diet
Can I drive after endoscopy?
It is commonly recommended that patients should refrain from driving for 24 hours after endoscopy in which sedation is given. … Whether patients can safely drive(e.g., home or to work) 1 hour after routine colonoscopy using propofol sedation is unknown.
What kind of anesthesia is used for endoscopy?
First, although the depth of sedation during these procedures is similar to general anesthesia, the airway is largely unprotected. Used as a sedative, propofol, the most popular agent used for these procedures has a narrow therapeutic window-transiting from mild sedation to deep general anesthesia rapidly.